Crop Improvement refers to the genetic alteration of plants to satisfy human needs. Main target of this method is to improve the appearance, quality and productivity.
- Plant Breeding
- Hybridization
- Polyploidy
- Protoplast Culture
- Protoplasmic Fusion
- Bio Fortification
- Tissue Culture
Crop Improvement involves two major approaches. Development of new or improved varieties and Improvements in management practices.

Plant Breeding

Plant Breeding is the purposeful manipulation of plant species in order to create desired plant types that are better suited for cultivation, give quality yields and disease resistant. There are two main types of plant breeding; Classical plant breeding and modern plant breeding. The classical plant breeding is followed by artificial selection to produce plants with desirable traits of higher yield, nutrition and disease resistant. Modern plant breeding uses modern technology in genetics, molecular biology and tissue culture.
Hybridization
Hybridization is the process of crossing two genetically different individuals to result in a third individual with a different set of traits. In agriculture it is vitally important to maintain a genetic diversity. There are four major types of hybridization;
- Intra-variety hybridization – Crosses between plants of the same variety
- Inter-variety hybridization – Crosses between plants of two different varieties of the same species
- Interspecific hybridization – Crosses between plants of two different species of the same genus
- Inter-generic hybridization – Crosses between plants of two different genera
Polyploidy
Triploid and tetraploid chromosomes are examples for polyploidy. Polyploidy cells and organisms contain more than two paired sets of chromosomes. Polyploidy can be the result of an autogenic multiplication of a plant genetic material or through hybridization, and is extremely common in domesticated crops. Polyploidy can be induced in plants and cell cultures by using some chemicals, the best one is Colchicine. Most polyploids show novel variation or morphological characteristics than their parental species. Many seedless fruit varieties are seedless due to the polyploidy. Many polyploidy crop varieties are preferred because they are sterile. Those crops are mostly propagated by vegetative propagation.
Protoplast Culture
The protoplast culture has unlimited potentialities for plant improvements. In future this method can be used for,
- The introduction of nitrogen – fixing bacteria and blue green algae into non-legumes; specially for cereals
- The induction of disease – resistance in a crop by the incorporation of a selective genome into the protoplast
- The induction and easy detection of mutations in haploid protoplasts
- Culture of protoplasts to raise clones for vegetative multiplication and for genetic diversity
Protoplasmic Fusion
Protoplasmic fusion involves physical union of fusion of protoplasts from two parents. Disease resistant ability, ability to undergo abiotic stress and other special characters can be induced by using this method. Plants can be maintained in the juvenile stage. Most of the agronomical important traits, such as cytoplasmic male sterility, antibiotic resistance and herbicide resistance, are protoplasmically encoded, hence can be easily transferred to other plant.
Bio Fortification
Bio fortification is the process by which the nutritional quality of food crops is improved through agronomic practices, plant breeding or modern biotechnology. Breeding crops with higher levels of vitamins and minerals or higher protein and healthier fats is the most practical method to improve public health.
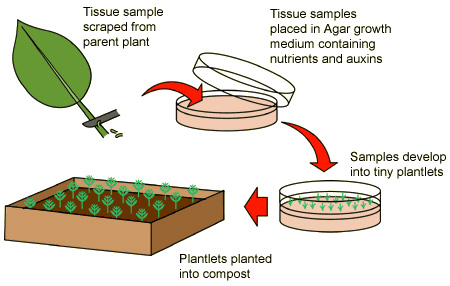
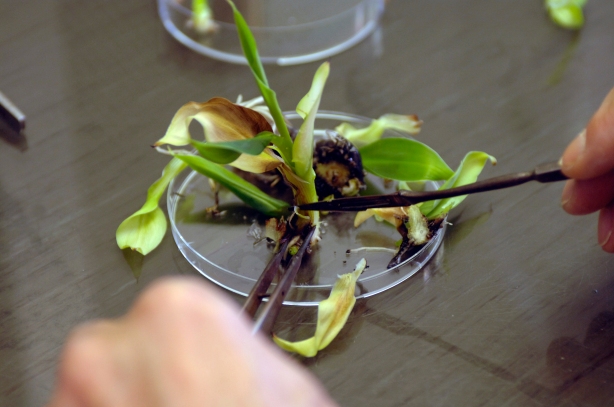
Tissue Culture
Plant tissue culture is a technique with which plant cells, tissues or organs are grown on an artificial nutrient medium, under controlled conditions. The basis of plant tissue culture is totipotency; the capacity of a living cell of a multi cellular organism to develop independently into an organism under favorable conditions. Some of advantages are,
- Micro propagation
- Production of disease free plants
- Genetic engineering
- Somatic hybridization